Postbiotics Supplements Make Prebiotic & Probiotics Obsolete

Postbiotics supplements now replace probiotics. Postbiotics are in food fermented by live bacteria. The best postbiotics products are found here, at SANESolution. Postbiotics with the proper organic acids and bioactive compounds allow for a myriad of health benefits that replace probiotics AND prebiotics. On this page you will learn what Postbiotics are, and why they are critically important for your health and weight management.
This flora through a fermentation process hen excretes a postbiotic product which can unleash health benefits such as:
- Byproducts Improve gut physiology
- Leaky gut repair
- Attend to inflammation (Anti Inflammatory response)
- Health effects like Boost or support immune response (also Anti Inflammatory)
Supplement index:
For ease of navigation through this SANESolution Health Guide (we go way beyond simple food sci and functional foods or suggestions), below is the table of contents.
- What Are Postbiotics (the probiotics and post-biotic working definition)?
- Metabolic products (organic acids) And How They Help You
- How are they Different From Prebiotics?
- Vs Probiotics
- Dietary Fiber (Foods field discussion)
- Gut Health Use
- Leaky Gut Use
- Inflammation Support
- Immune Response Byproducts
- Why Harvard Calls Butyrate the “Optimal” of Postbiotics
- Postbiotic Foods? Not From Your Diet!
- Butyrate: Why TRIButyrate is the Best Way to Get Butyrate
- Supplement Information We Recommend For Humans
the supplement guide
100 trillion microorganisms, mostly bacteria, live in your gastrointestinal tract. These microorganisms, called “gut microbiota,” or gut microbiome, were once thought to control digestion, nutrient absorption, and excretion.
But research now shows that an imbalance of good and bad intestinal bacteria (dysbiosis) has been linked to many poor health outcomes and medical conditions including Obesity, Diabetes, and Chronic kidney disease 1,2 Multiple studies also show that having a diverse microbiome is crucial to overall health.3,4
So, postbiotics waste products not probiotics?
If you’re wondering what these compounds are, you’re not alone. Postbiotic is a fairly new term in microbiology. As you’re probably more familiar with prebiotics and probiotics, we’ll start there. Probiotics / prebiotics increase the number and diversity of beneficial microbes or microbiota.
Postbiotic products from bacteria are “waste” metabolic products left behind from the interaction between prebiotics and probiotics. They are a result of “good” fermentation inside your colon which provides health benefit to our immune system.
The difference between prebiotic or probiotics types
Specifically, when you consume fiber from food, it travels to your lower intestine (colon) where it is eaten (fermentation ) by your good probiotics. This bacteria then excretes postbiotics. You can check out Runner’s World comparison of prebiotic, probiotics, and postbiotic as well as Dr. Axe’s description of their differences at great length to get a better idea!
Metabolite products (bioactive compounds)
These postbiotic metabolites are the products created from the probiotic fermentation . More than 22,000 metabolites are identified in scientific literature.5
Various postbiotic components have been shown to have the following potential benefits such as Anti-obesity, Anti-inflammatory, and Antioxidant properties.
Health benefits may even extend to:
Lowered blood pressure, reduced cholesterol levels, and a regulated immune system response. A postbiotic may even have a direct impact on health, providing a host of beneficial human health effects.6
Most-studied metabolite types
Along with some of their positive effects with health-regulating benefits (talk about benefits to the host!), the postbiotic plays a role in some of the most complex immune function pathways from cell to cell interactions.
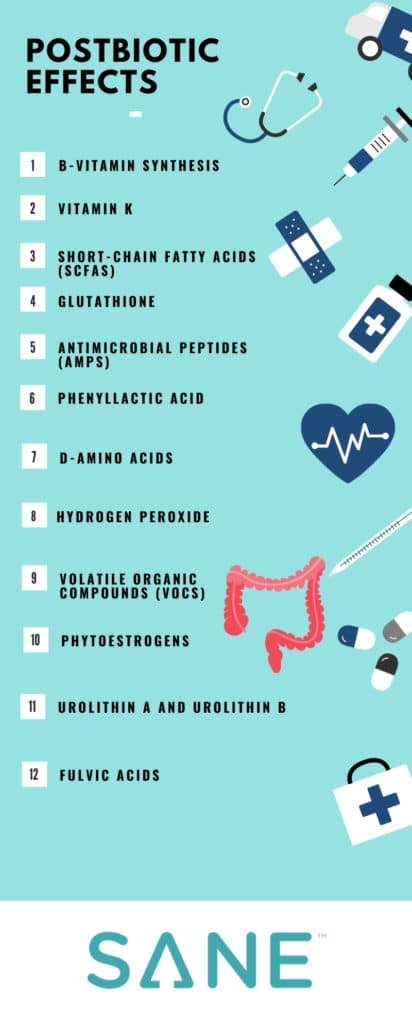
12 Postbiotics Product Benefits to the Host:
B-vitamins synthesis: (biotin, cobalamin, folate, nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, riboflavin, and thiamine)7.
Vitamin K: Essential for proper blood clotting and bone metabolism. It also regulates blood calcium levels.
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs): acetic, propionic and butyrate.9: They provide important functions in your body.10
Glutathione 11: Postbiotics may reduce the risk of several diseases – including diabetes, cancer, and rheumatoid arthritis – by reducing oxidative stress.12 (Oxidative stress in the cells occurs when the body cannot fight off free radicals sufficiently.)
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) 13: Postbiotics may protect the body against dangerous pathogens. And unlike traditional antibiotics, antimicrobial peptides appear to slow pathogenic resistance to them.14
Phenyllactic acid 15: Postbiotics may and have shown antibacterial properties against various bacteria.
D-amino acids 16: Appear to have bacterial regulatory properties.
Hydrogen peroxide 17: Has been shown to have antibacterial properties that may help you fight off infection.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) 18: Postbiotics may serve as a marker for the presence or absence of certain harmful microbes.
Phytoestrogens: equol, enterolactone, enterodiol 19: Mimics the female hormone estrogen in the body, which can modulate the symptoms of menopause.
Urolithin A and Urolithin B 20: Like phytoestrogens, they may display behavior that mimics that of estrogen in the body.
Fulvic acids: Helps carry nutrients into the cells. Thus, fulvic acids may lessen free radical damage, among other things. 21
Prebiotics and probiotics difference?
Prebiotics are the food sources of beneficial colon residing microbes. There are key differences between POST and Prebiotics, although their relationship is interdependent.
Prebiotic food contain dietary fibers that pass through the upper part of the digestive system intact because the body cannot break them down. POST is a byproduct created from prebiotic fermentation.
Prebiotics are typically found in foods
You get prebiotics from your diet. Great sources of health-promoting prebiotic foods include Leeks, Asparagus, Onions, Chicory root, Dandelion greens, and Garlic.
You can also take prebiotic supplements.
Why probiotics are replaced
There’s really no comparison between the two as their promoting and beneficial effects on the human body drastically differ. A Post-biotic is created when “good” microbes ferment dietary fiber in the colon. (Good bacteria = probiotics. Dietary fiber = prebiotics.) You can also get beneficial bacteria from probiotic supplements.
Good Bacteria = Probiotics and Dietary Fiber = Prebiotics
Probiotics foods are created from fermentation and thus contain live microbes (live microorganisms) that can help benefit and rebalance your intestinal bacteria.
When it comes to the intestines and the immune system, the beneficial effects of them may help the cells lining our digestive system. The health benefits of their waste products, aka postbiotics, include promoting pathways that are deeply linked with our total body immunity. Also, because they’re not live, they’re more stable and have a longer shelf life than probiotics.
This is also true for some of these digestive health supplements. For instance, doctors at Harvard Medical School call butyrate the “optimal” fatty acid and note that it “shows a higher potency” and added health benefits.23
Promoting Probiotics-rich food:
Probiotic-rich fermented foods include:
- Tempeh, made from soybeans
- Miso, made from barley, soybeans, or rice
- Yogurt, made from milk. To ensure the brand you’re buying is a probiotic, check the ingredient label and make sure it includes L. acidophilus.Kefir, a type of fermented milk
- Buttermilk. To ensure you’re getting probiotic buttermilk, make sure the label says the product contains “active cultures”.
- Sauerkraut, made from cabbage
Dietary fiber dairy foods or prebiotics foods:
To get these SCFA’s you can, of course, load up on dietary fiber from food intake. This will perhaps slightly increase the amount of compound yielded from fermentation from our microbiota.
Only then does your colonic microbiota biome or bacteria digest the fiber, fermenting it in your colon. (This is why you often experience painful bloating and embarrassing gas when you eat more fiber.)
You can also get this form of biotic directly from certain nutrition foods, such as butter and ghee. But the amount you’d get is even less than that created through probiotic fermentation.
Postbiotics product positive effects on your intestines
If you’re read this far, you know that these postbiotics are more than just a term within the functional medicine field. Postbiotics as nutraceuticals are great for digestive health.
How effective are postbiotics for stomach-related issues?
Very! Let’s start with an increasingly common gastrointestinal condition — irritable bowel syndrome.
Postbiotics and IBS
According to the International Foundation for Gastrointestinal Disorders, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is the “most common functional gastrointestinal (GI) disorder.”25 IBS affects as many as 45 million people in the United States.26
According to a 2013 study, this SCFA can reduce the hypersensitivity of intestinal receptors, resulting in a decrease of pressure inside the intestines.28 This may help in reducing the pain and bloating of IBS. It can also ease constipation by helping the bowel muscles contract and retract properly.29
Benefits of postbiotics include leaky gut:
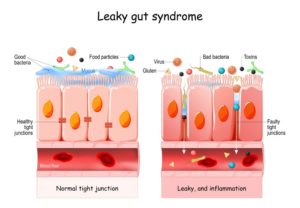
As with IBS, postbiotics contain compounds that may also help fix leaky gut, a condition that plagues so many people. How do your walls become “leaky?” It starts with your intestinal wall. A layer of cells line your intestines, making up your intestinal wall.
These cells are connected by gates that are called “tight junctions”. These gates allow water and nutrients to enter your colon, while also keeping toxins and other harmful substances from escaping into your bloodstream. This is known as the gut barrier, and it’s extremely important for your health.
Leaky gut syndrome may lead to:
Irritable bowel disease, Crohn’s disease, Diabetes, Food allergies, Polycystic ovary syndrome, Anxiety, Depression, Fatigue, Headaches, and Joint pain.35
Basically, postbiotics make sure your gut cells have what they need to keep the “gates” functioning perfectly.36 In essence, they support gut barrier function. Research also show that postbiotics directly influence the intestinal bacteria, helping to balance colonic bacteria.
Postbiotics may help lower and have positive effects on inflammation:
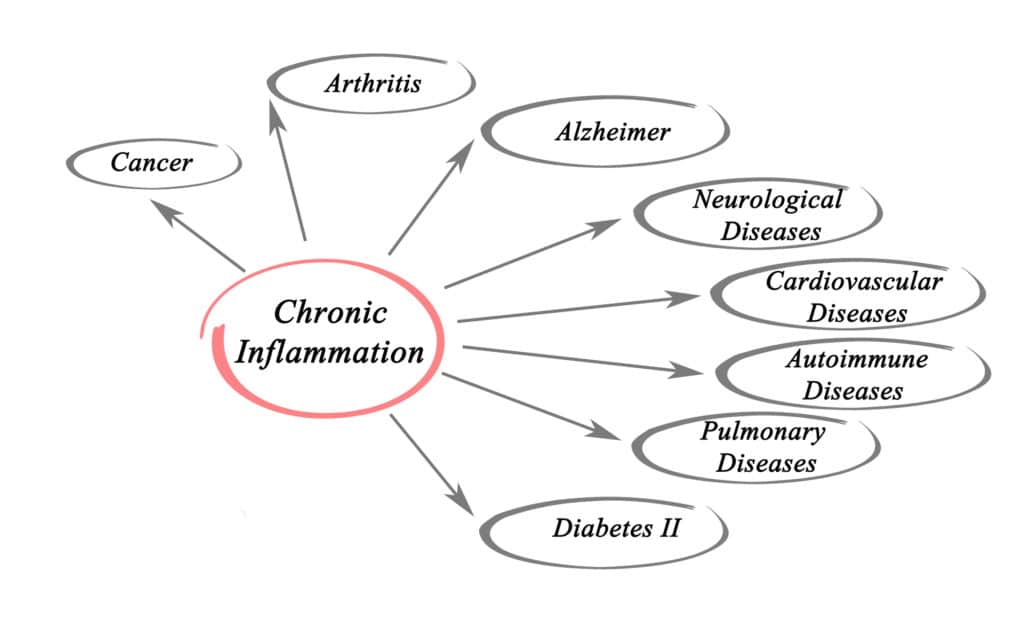
Butyric acid obtained from postbiotics is one of the gut colonic supplement that can help with general inflammation. This is important because systemic inflammation has become a villain in medicine.
Chronic inflammation has been associated with a wide range of health conditions and diseases, including: Obesity, Heart Disease, Diabetes, Metabolic syndrome, Psoriasis, Inflammatory bowel disease, and Asthma 39
Postbiotics and inflammatory responses:
Postbiotics can help regulate your immune response, which can reduce or eliminate systemic inflammation. Before we continue, it’s important to know that inflammation isn’t always a negative occurrence.
One of the immune system’s most important weapons is inflammation. When the immune system detects an intruder — pathogens, toxins, and other foreign bodies — it launches an attack to kill it. It’s first line of defense is inflammation, which traps the intruders so that they cannot travel to other parts of the body.
This type of acute inflammation is characterized by swelling and redness at the site of the invasion/infection. White blood cells then move in to fight the infection and heal the injury. As the body heals, inflammation gradually recedes and then disappears.
White blood cells then move in to fight the infection and heal the injury. As the body heals, inflammation gradually recedes and then disappears.
The problem is when inflammation continues
Chronic long-lasting inflammation can happen for a number of reasons, including hypersensitivity to harmless substances, long-term medical condition such as arthritis, or long-term, low-level exposure to toxins.
But intestinal or gut health promoting postbiotic metabolites can help. Research shows that these postbiotics can calm and quiet your immune system by down-regulating your T-cells. (The t-cells are a type of white blood cell that is crucial in the adaptive immune response.46
Why Harvard Calls Butyrate “Optimal”
Harvard calls butyrate the “optimal” postbiotics primarily because of its effect on histone deacetylases (HDACs). In a 2018 Harvard study, researchers found that post-biotic (specifically butyrate) keep colonic epithelial stem cell line from rapidly multiplying. 47(Epithelial stem cells multiplying could lead to tumors and eventually colon cancer.). It also suppresses inflammation, which inhibits the activity of HDAC.
Researchers concluded that butyrate is the strongest inhibitor of the activity of HDACs, among the short-chains. 48
This is one of many studies that show that butyrate may defend against colon cancer. Another reason for this effect is that butyrate is the main source of energy for cells that line the colon. This is true even when glucose is present.49
Why Postbiotics TRIButyrate is the best
After years of research, scientists have combined 3 Butyrate molecules with a glycerol molecule to create a radically more effective version of this “optimal” short-chain fatty acid.50 And that’s how TRIButyrate was created.
There are several supplements for gut health on the market today. Research clearly shows, Viscera-3 is superior to any other post-biotic brand.
With Viscera-3, this superior form of TRIbutyrate is time-released directly into your lower colon (the only place it can provide all the above life-changing gut health benefits). It is three times more potent than the weak short-chain fatty acids created by fiber alone.
This patented nutrient is the fastest, easiest and most effective way to poop a more normal, healthier stool and enjoy a slimmer, less bloated waist in just 48 hours!
Give this postbiotic a try and see for yourself today!
POSTBIOTICS REFERENCES:
You can locate the full list of references for this guide on our medical bibliography page that is updated frequently! SANE Rights Reserved








Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!